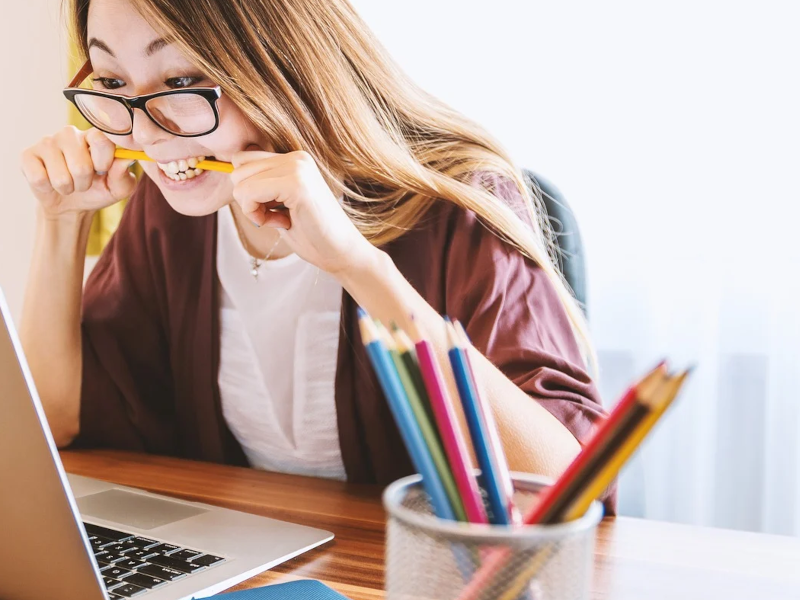
Anchoring bias is the tendency to make logical decisions from a particular reference point. The first piece of information is given a strong significance level mainly when there is no other evidence during decision-making. Based on the limited information, we tend to think that this information is a logical estimate. When more information is given, this effect can also be caused. The anchor can have an overwhelming impact on your decision can be caused by the anchor even if you have detailed information to make an informed decision.
Where this bias occurs
Anchoring occurs on several different practical occasions, such as:
• Negotiations
Anchor has a significant effect on negotiations, as recent research from Harvard University indicates. As we buy or sell, we tend to wait for a first offer from the other party. The negotiation can be skewed by this effect, as proven. As the research states, a strong anchoring effect can be caused by the first offer in situations of uncertainty and significant ambiguity. The first offer exerts a strong pull throughout the negotiation, thus setting the ground for negotiation. Higher sales are likely to be led by the first higher offer than lower first offers.
For example, a car dealer sells a car at ![]() 25000. The car dealer gives the customer an offer of
25000. The car dealer gives the customer an offer of  33000 at the same time. The dealer offers the customer a
33000 at the same time. The dealer offers the customer a  33000 will seem to be a good deal when the customer already anchors the price expectation for the car.
33000 will seem to be a good deal when the customer already anchors the price expectation for the car.
• Courtroom
Anchoring bias is linked to the courtroom, where judges award identical crimes with different sentences. It can be either the bail or the number of years. The judge’s final verdict can be impacted if an initial sentence is recommended. Longer sentences are given when unrealistic high penalties are provided as an option to the judges, according to research by Thomas Mussweiler and Birte Englich. Judges and other people are susceptible to anchoring even if there is available information.
• Marketing
The essential tool to help you increase sales in advertising and marketing is the anchoring bias. To ensure that you take advantage of anchoring bias, you need to use several key techniques. Having frequent discounts on the products you made artificially high is a crucial technique. People see a good deal in the discounts on goods whose price has been highly anchored.
• Showroom sales
Shown room displays the most attractive and expensive cars to encourage buyers. The customers see the highest price first, which is crucial before being drawn in. The comparison that comes out after anchor is placed on the prices of the luxurious car makes the customer think that the price is going to be cheap for every other vehicle. The agility of the customer to pay for the vehicle is increased by higher prices.
How to Avoid Anchoring Bias
1. Acknowledgment
Acknowledging that anchoring bias exists is the first step to avoiding it. You may prevent being trapped by the set bias when you recognize that such influences are susceptible to your mind. You will beat the seller of an item by not allowing the other party to make the first offer as the anchor or going into a negotiation.
2. Step back and take your time
Before making a decision, it is essential always to take your time. A bigger picture is portrayed when you step back to acknowledge the anchoring bias. The anchoring bias effects are diluted because you have more information after taking time during decision-making. The price of goods sold at an offer of 25% off may be the same price in another store. Because of that reason, you need to acquire more information by stepping back and acknowledging that the data is limited for decision making.
3. Beat the anchor
Counteracting anchor is essential when you understand why and how it exists. You can make better decisions by knowing about its existence. Dropping the anchor price first gives you the advantage of starting a negotiation hence the price dictation is in your hand. The price will always favor you even though the results are not what you desired.
Why Is Anchoring Bias Important
Your perspective can be skewed, and clinging to a particular value can be influenced by bias when deciding on a reasonable budget or schedule for a project hence the most persuasive tendencies. The value or decision decided may be irrational.
The time we require to complete a project and the cost tend to be estimated; this is known as the planning fallacy. You are anchored to the cost and time you set; hence you are reluctant to change or update the plan. Due to the money tied up in the venture, the business industry can result in significant consequences.
Conclusion
It is the cognitive bias where the first information is strongly relied on to decide on a particular topic. The importance of keeping anchoring bias in mind is that it helps you gain confidence during any negotiation. You need to understand how to avoid being anchored by this cognitive bias. Always take time to make a decision and do not be persuaded by the anchored prices.

